
Practical guide to neonatal cranial ultrasound (CrUS) basics Paediatrics and Child Health
Antiamyloid antibodies have been used to reduce cerebral amyloid-beta (Aβ) load in patients with Alzheimer's disease. We applied focused ultrasound with each of six monthly aducanumab infusions to temporarily open the blood-brain barrier with the goal of enhancing amyloid removal in selected brain regions in three participants over a period of 6 months.

Normal neonatal brain sonography in frontal coronal plane at the level... Download Scientific
Clinical Indications for Cranial US A fundamental understanding of normal neonatal neuroanatomy is required for appropriate image interpretation. The online presentation reviews normal imaging findings at cranial US with an emphasis on a systematic approach and anatomic landmarks.

Normal neonatal brain sonography of a preterm newborn in sagittal... Download Scientific Diagram
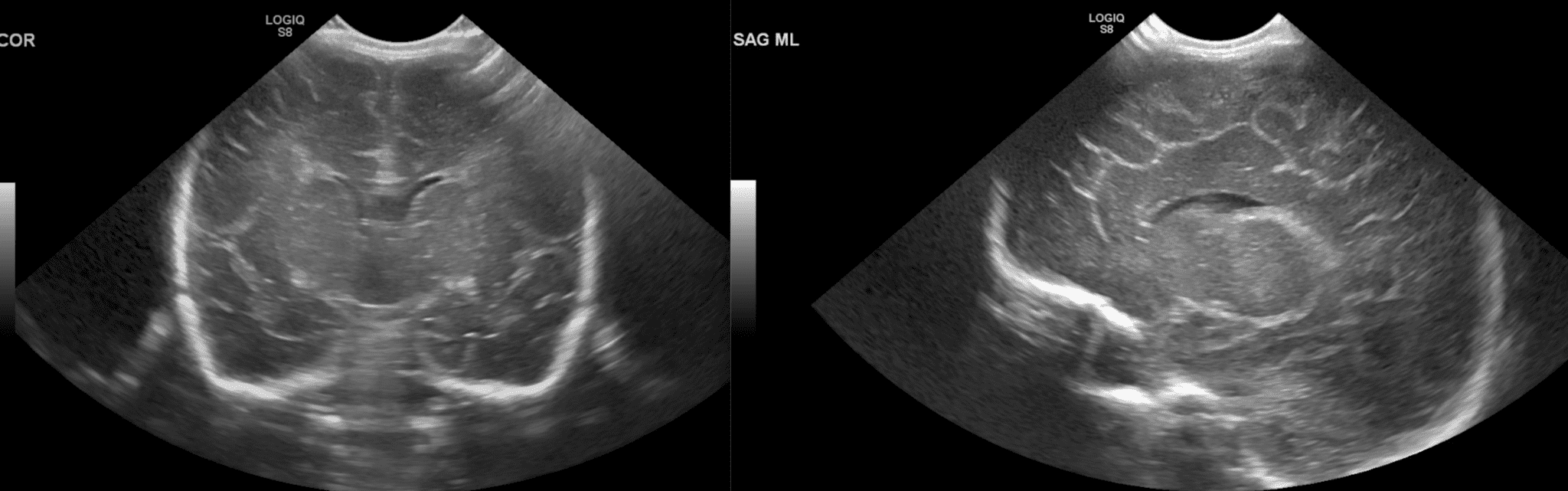
Ultrasound is an exceptional tool for the evaluation of an infant's brain. It is portable and can be easily and quickly performed at the bedside. Therefore, the initial imaging modality used to evaluate the intracranial anatomy and identify intracranial pathologies such as congenital anomalies, intracranial hemorrhage, ischemia, and hydrocephalus, especially in sick preterm infants.

Infant Head Ultrasound Anatomy dbabyzi
Cranial sonography has highest impact in neonates suspected to have meningitis and its complications; perinatal ischemia particularly periventricular leukomalacia (PVL); hydrocephalus resulting from multitude of causes and hemorrhage. Not withstanding this, cranial sonography has yielded results for a repertoire of indications.

Neonatal brain sagittal midline Neonatal, Ultrasound, Sonography student
Ultrasound imaging of the head uses sound waves to produce pictures of the brain and cerebrospinal fluid. It is usually performed on infants, whose skulls have not completely formed. A transcranial Doppler ultrasound evaluates blood flow in the brain's major arteries. Ultrasound is safe, noninvasive, and does not use ionizing radiation.

Ultrasound fetal brain image from left to right the columns show the... Download Scientific
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data. Transcranial Doppler ( TCD ) , also known as transcranial color-coded duplex sonography ( TCCS) is a sonographic study of intracranial structures and blood vessels, used most commonly to identify the hemodynamic state present in the vertebrobasilar circulation and the circle of Willis .

Normal neonatal brain sonography of a preterm newborn in right lateral... Download Scientific
Abstract Cranial ultrasound (CUS) is an extremely valuable tool to evaluate the brain during the first year of life, in experienced hands. It is the initial screening imaging tool to evaluate the infants' brain and complementary to the use of computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
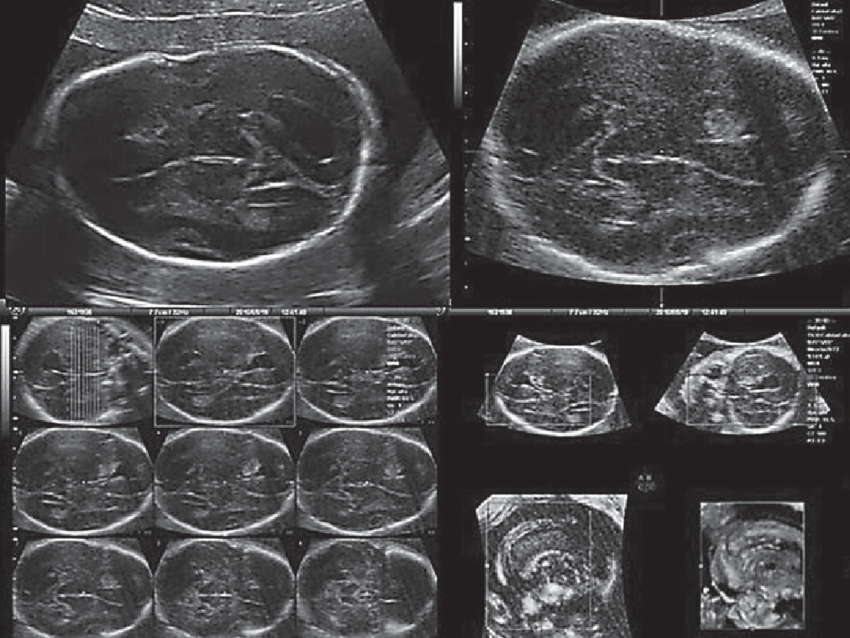
Case 2 2D and 3D fetal brain ultrasound showing marked ventricular... Download Scientific Diagram
00:37 Above. Normal fetal CNS at 22 2/7ths weeks. Video courtesy of Dr. Mayank Chowdhury; Pallav Imaging Institute, Mayflower Women's Hospital, Ahmedabad, India. Above. Key fetal anatomy includes the choroid plexus, the septum cavum pellucidi (SCP), the lateral ventricles, and the corpus callosum.
Cranial Ultrasound UAMS Department of Radiology
Introduction Cranial ultrasound is a valuable screening and diagnostic examination with distinct advantages compared to alternative imaging modalities, particularly in the young child. These advantages include easy accessibility, relatively low cost, no radiation, and a short examination time.

Coronal section of brain The BMJ
Head ultrasound (HUS), also called cranial ultrasound (CUS), is obtained for the diagnosis and follow-up of premature and sick neonates. Advantages Head ultrasound has the advantages of: accessibility mobility, i.e. bedside scanning at the NICU and neonatal ward requiring no sedation

cranial ultrasound anatomy
In this chapter, we will discuss ultrasound anatomy of the neonatal brain, how to differentiate normal findings from (subtle) abnormalities, the optimal timing of ultrasound examinations, and the most frequently occurring brain lesions of the preterm infant. 3.1 Ultrasound Anatomy of the Neonatal Brain

Practical guide to neonatal cranial ultrasound (CrUS) basics Paediatrics and Child Health
Our study explores the topography of the brain on B‐mode ultrasound in adult critically ill patients and provides descriptive examples of the anatomical and pathological structures that can be visualized on B‐mode cranial ultrasonography.

Practical guide to neonatal cranial ultrasound (CrUS) basics Paediatrics and Child Health
Chronic abnormality of intracranial anatomy. intracranial hematoma (back to contents) Intracranial hematomas will appear hyperechoic for about five days. Subsequently, they will become hypoechoic, with a surrounding hyperechoic halo.. Venkatraghavan L. Clinical applications of point-of-care ultrasound in brain injury: a narrative review.

Fetal Brain Anatomy
Brain ultrasonography can be used to evaluate cerebral anatomy and pathology, as well as cerebral circulation through analysis of blood flow velocities.

Infant Head Ultrasound Anatomy dbabyzi
In the past three decades, cerebral ultrasound (CUS) has become a trusted technique to study the neonatal brain. It is a relatively cheap, non-invasive, bedside neuroimaging method available in.

Ultrasound and MR Imaging of the Normal Fetal Brain Neuroimaging Clinics
Several studies have shown that focused ultrasound can safely and transiently open the blood-brain barrier in patients with Alzheimer's disease and other neurologic disorders. 3-13 The effect.